
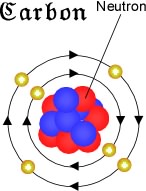
In the 17th century, the Anglo-Irish chemist Robert Boyle ( – ) was the first scientist who discovered carbon as an element that cannot be further broken down into other substances. But, despite the fact of carbon being discovered far before the times of modern chemistry, many chemists have attempted to determine both the chemical and physical properties of carbon by studying and experimenting with its various forms and compounds in much more recent times. It can be dissolved by acids and bases, but it’s insoluble in water.Ĭharcoal and soot were familiar to the ancient civilizations way before our times. When exposed to high temperatures, carbon burns brightly. Carbon is an excellent conductor of electricity, possesses great thermo-insulating properties, and is extremely durable. This tetravalent member of the carbon family of elements in the periodic table is able to form covalent chemical bonds. However, both the chemical and physical properties of carbon depend on its allotropic structure, which makes it one of the most unique and versatile chemical elements. With oxidation states of +2, +3, +4, and the highest sublimation point among all elements, carbon has an electronegativity of 2.55 according to Pauling, whereas the atomic radius according to van der Waals is 170 pm. With a melting temperature of 3500 ☌ (3773 K, 6332 ☏), carbon has the highest melting point among the periodic system elements. Carbon is a polyatomic nonmetal with a hexagonal crystal structure that reaches its boiling point at 4827 ☌, or 5100 K (8721 ☏). This star-born substance has the periodic table symbol C, atomic number 6, variable atomic mass from 12.0096 to 12.0116 g.mol -1, and electronic configuration 2s2 2p2. The energy of the second ionization: 2351.9 kJ.mol -1ĭiscovery date: In ancient times by an unknown discoverer The energy of the first ionization: 11.2603 kJ.mol -1 Most characteristic isotope: carbon-12, carbon-13 (both stable and naturally occurring isotopes), carbon-14 (a radionuclide) Physical state: Solid non-metal at room temperatureĮlectronegativity according to Pauling: 2.55īoiling point: 4,827 ☌, 5100 K, (8,721 ☏) Period: 4 (Carbon family: carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, and lead)Ĭolor: It depends on the carbon allomorph (the colors palette includes the following nuances: transparent/colorless, white, black and shiny, dark brown, or black) The symbol in the periodic table of elements: (C)Ītomic weight (mass): 12.0096 to 12.0116 g.mol -1 Fact Box Chemical and Physical Properties of Carbon


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
